How about chisels?
Chisels are simple cutting tools, set in motion by hand pressure, a mallet or hammer blow, used to work wood. Chisels are simple cutting tools, set in motion by hand pressure, a mallet or hammer blow, used for woodworking.
The chisel consists of a steel profile, a blade and a handle. The blade has a sharp edge on one side and a spike on the other side, on which a plastic or wooden handle is hammered. If the handle is wooden, it is made of beech, hornbeam or other hard wood. The handles of some types of chisels are equipped with steel rings on one or both sides, preventing the handle from splitting or cracking when struck with a mallet.
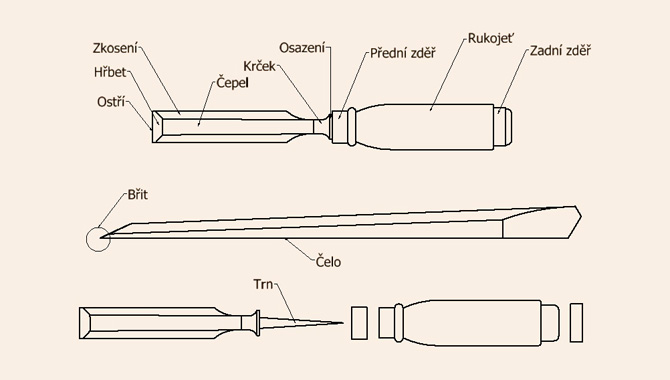
In the course of time, many different fields dealing with woodworking have emerged, where each field has its own types of chisels, which are somewhat specific.
Carpenter's chisels
Straight and straight edged chisels
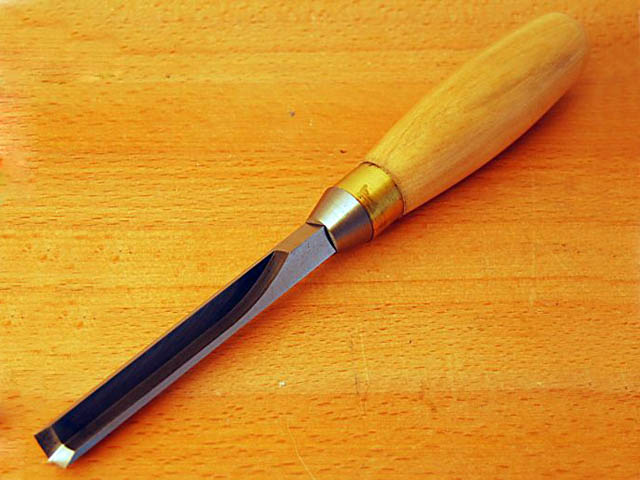
Straight are chisels with a long and solid blade that is not beveled on the sides. Their advantage is great strength, they can withstand strong blows with a mallet. Their use is universal, they are especially suitable for rougher work. Manufactured in widths of 3-50 mm.
Straight edged are chisels that have a chamfer on both side edges, which allows them to get into narrow and hard-to-reach places. Edged chisels are mainly used for the production of joinery joints. They are available in widths of 3-50 mm.
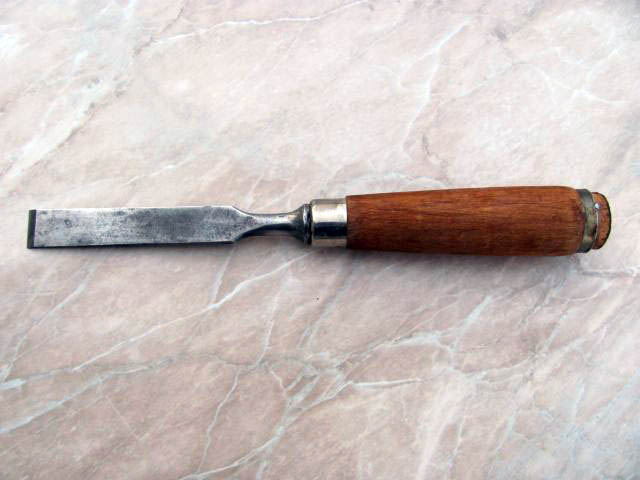

Straight chisel
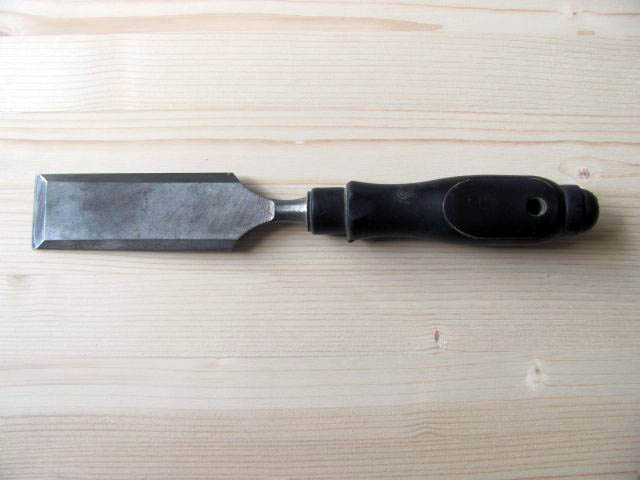

Straight edged chisel
Hollow chisels
they are suitable for punching out round or rounded holes or jamming round edges of building fittings. It is produced in widths of 5-40 mm.
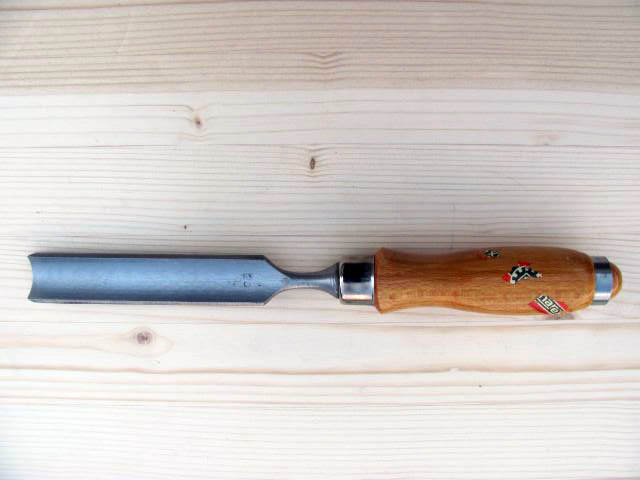

Narex hollow chisel
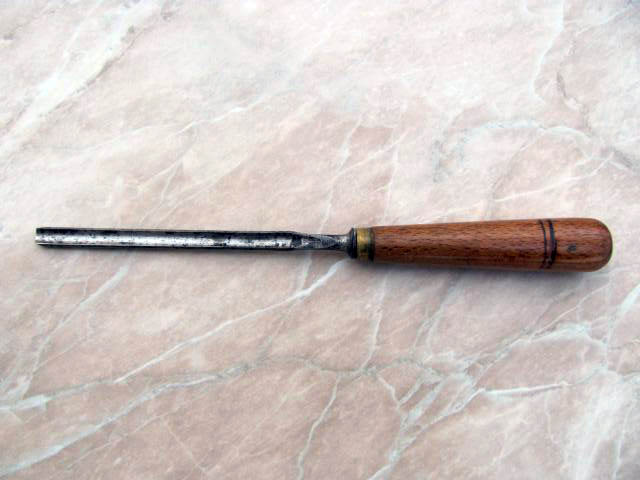

Narrow hollow chisel
Tapping chisels (punchers, perforators)
are strong chisels, intended for precise cutting of joinery joints and for gouging to a greater depth. The tenon chisel is selected so that its width corresponds to the width of the mortise hole. They are produced in widths of 2-20 mm.
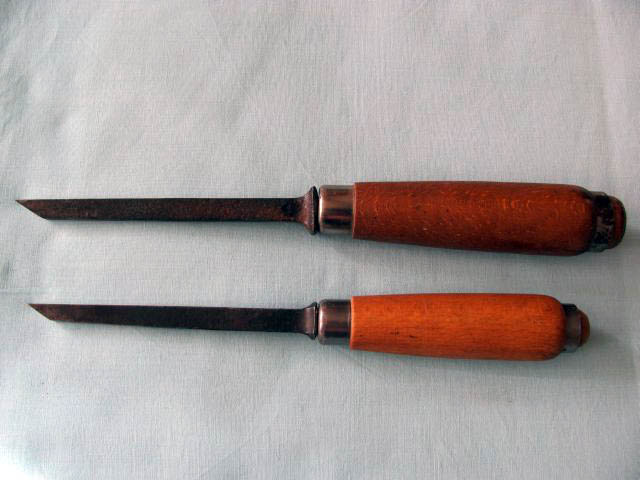

Pin chisels - hole punches
Sinking chisels (cross hole punches)
are chisels intended for cutting holes for window and door hinges. They are single-pointed, double-pointed or three-pointed, 1-3 mm thick, 24-34 mm wide. The strength of the chisel is chosen according to the strength of the metal hinge.
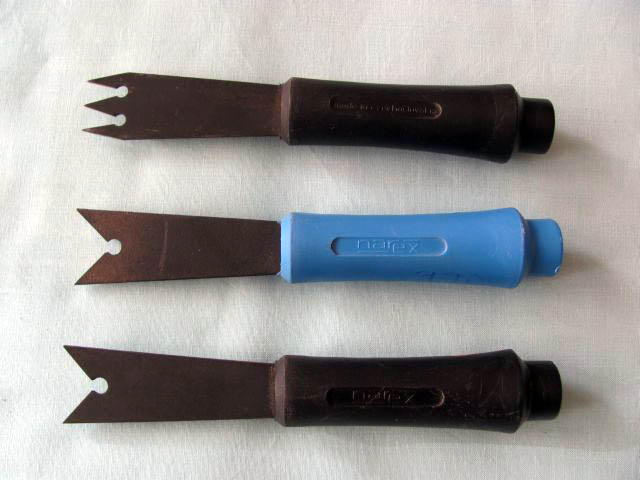

Narex double-edged and triple-edged countersunk chisels
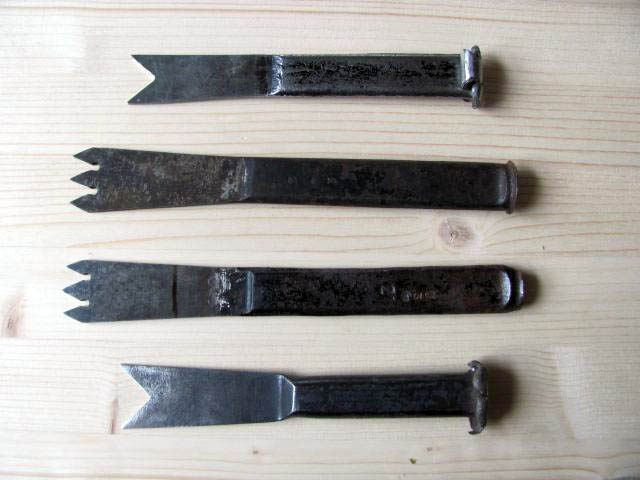

All metal countersunk chisels
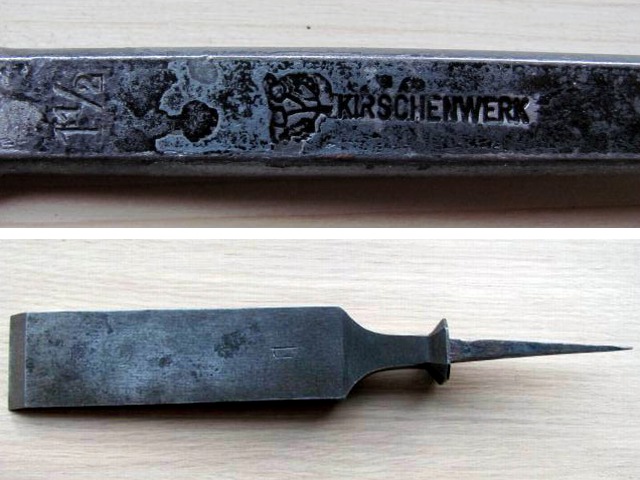

Marked on countersunk chisel and straight chisel without handle
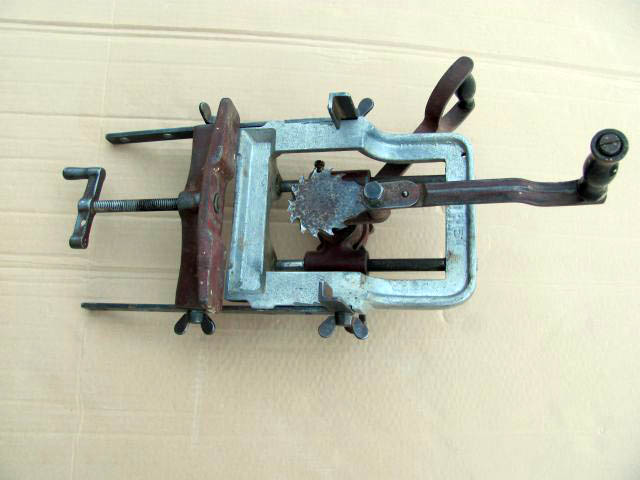

Preparation for embedding window and door curtains
Lock chisel (lock punch)
is a steel narrow chisel with two arms bent at right angles, with a blade on each arm. The blades are perpendicular to each other. It is used to embed locking mechanisms in otherwise inaccessible places.
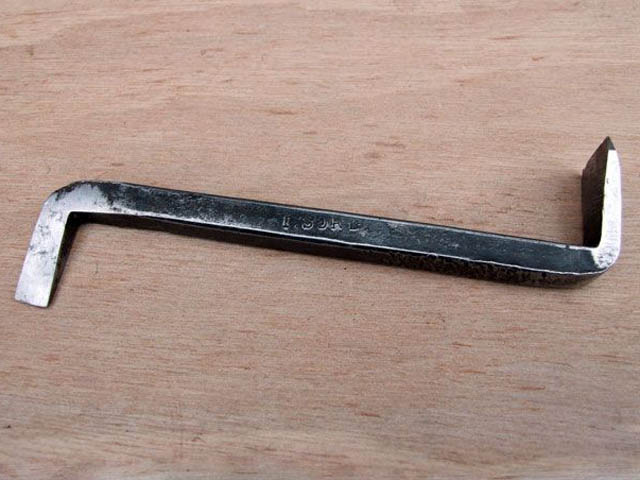

Lock Chisel
Slanting chisels
are chisels intended primarily for cleaning material in corners or other hard-to-reach places. They are right or left, the bevel is about 30 degrees. They are produced in widths of 6–30 mm.
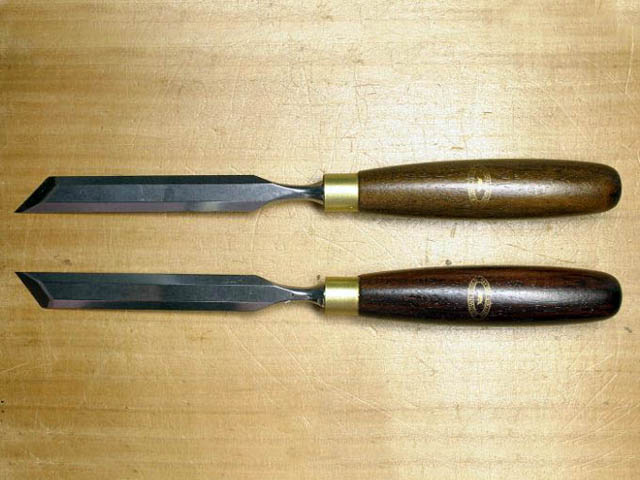

Bevel chisels
Corner chisels
they are intended for cleaning the corners of mortises or for precise rectangular alignment of the corners of openings.

Corner chisel
The angle of the edge of joinery chisels is approx. 25-30 degrees, depending on the hardness of the processed material. The softer the material, the sharper the angle we grind.
Carpenter's chisels
In carpentry, flat chisels with edges, without edges and hole punches are used.
These are similar chisels to carpentry chisels, only they tend to have a stronger handle, a stronger blade compared to carpentry chisels, and overall they can be longer.
Carving chisels
Carving chisels can be divided into straight and longitudinally curved chisels. Longitudinally curved chisels are further divided into long curved and short curved /spoon/. Curved chisels are especially suitable for work in greater depths and hard-to-reach places.
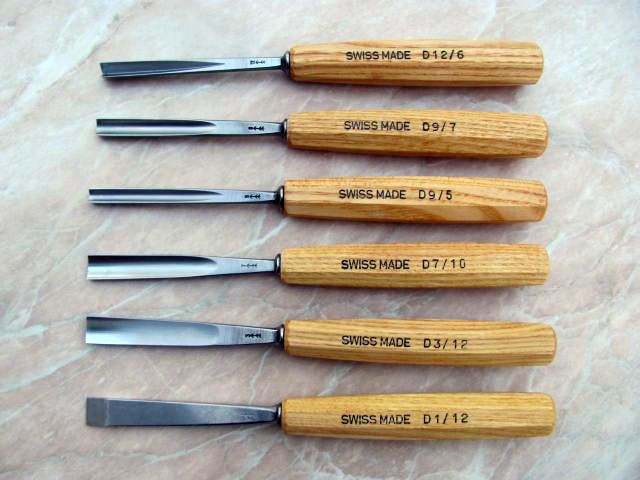

Pfeil carving chisels
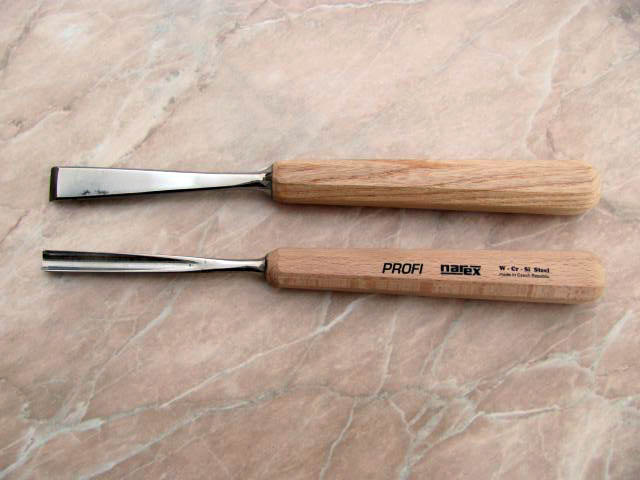

Narex Carving Chisels
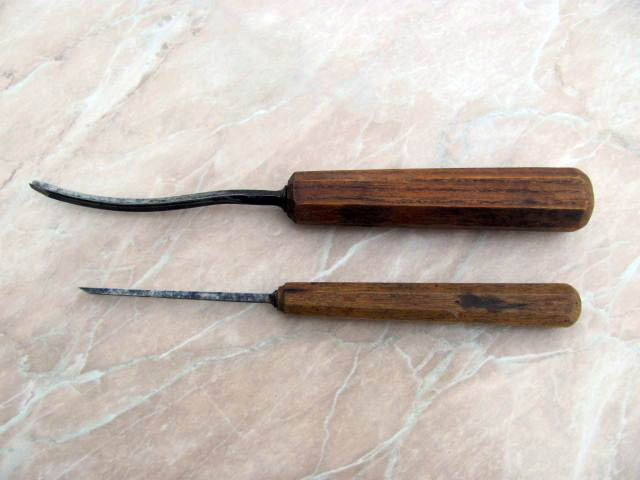

Old carving chisels
The blades of carving chisels have different profiles, from straight, to slightly convex, to very deep.
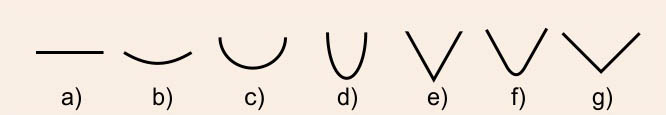
a) straight profile, b) shallow profile, c) half-round profile, d) deep profile, e) 60° profile, f) 60° rounded profile, g) 90° profile
The handles of carving chisels are wooden, barrel-shaped, often octagonal for a better grip of the chisel when working.
The angle of the carving chisel blade is approx. 17–27°, depending on the hardness of the material. When cutting different types of wood, we choose a universal angle of approx. 24 degrees.
Sculpture chisels can also be classified as carving chisels. These are actually wide carving chisels, intended for larger objects.
Turning chisels (lathes)
Turning chisels have a longer blade than carpentry chisels, which smoothly transitions into a mandrel for fixing the handle. Turning chisels do not have a neck or shoulder for a better impact of the handle close to the blade. Overall, they are longer compared to other chisels, which allows for a better grip with both hands and better guidance on the support when turning by hand.
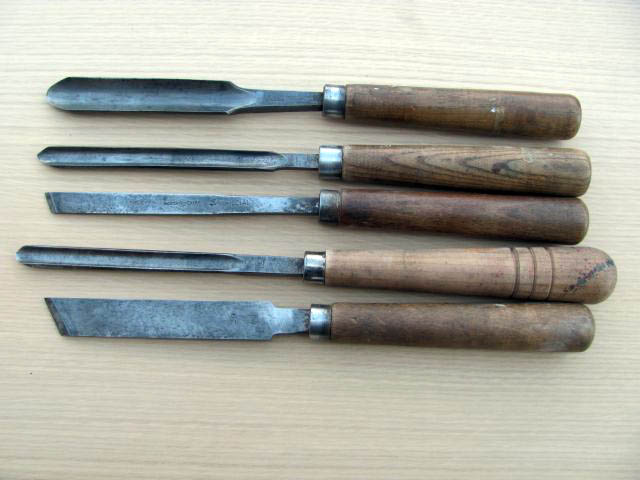

Pfeil carving chisels

Narex Carving Chisels

Old carving chisels
Basic types of turning chisels:
Removing chisel
is a universal chisel, larger diameters are suitable for larger material removal and coarser turning, smaller diameters are suitable for turning precise round shapes.
Stroke Chisel
it is suitable for turning straight or convex surfaces and their cleaning and for turning "V" shapes, various recesses and for dividing material.
Cavity Chisel
This chisel is mainly used for turning hollow shapes and bowls, sometimes also called a bowl chisel. It is suitable for transverse turning. Its construction enables the removal of a larger amount of material even in deep cavities.
Going Chisel
It is used for dividing material or creating grooves.
Flat chisel
it is suitable for cleaning round shapes, it is also suitable for turning bowl-shaped shapes across the threads.
Plunging Chisel
Chisel intended for the production of various notches and cleaning.
Internal removal chisel
A chisel specially designed for turning the internal shapes of containers. It can also be used for dividing material.
The angle of the blade of turning chisels is approximately between 20-80 degrees, depending on the type of material used, the type of chisel and the turning technique.
Special chisels
There are many other types of chisels designed for woodworking, most of them are already manufactured specifically for a specific operation or the production of a specific wooden part.
For example:
Fiddler's Chisels
- Chisels intended for makers and repairers of musical instruments and violinists.
- hollow spoon chisels for the production of stringed musical instrument plates
- chisels for processing necks and screws
- chisels for making deep grooves when fitting cello, double bass or guitar necks to bodies
- special chisels designed for making and repairing bows
Chisels used in foundry making models
Long spoon chisels /flip-flops/ - with these chisels, the blade turns into a long rod with a handle. The rod is curved like a spoon, for more convenient carving of internal surfaces and various configurations.
Whetstones
Grinding stones and grinding wheels are also worth mentioning.
When sharpening straight chisels, it is sufficient to use two grinding stones, coarse and fine (wrapping).
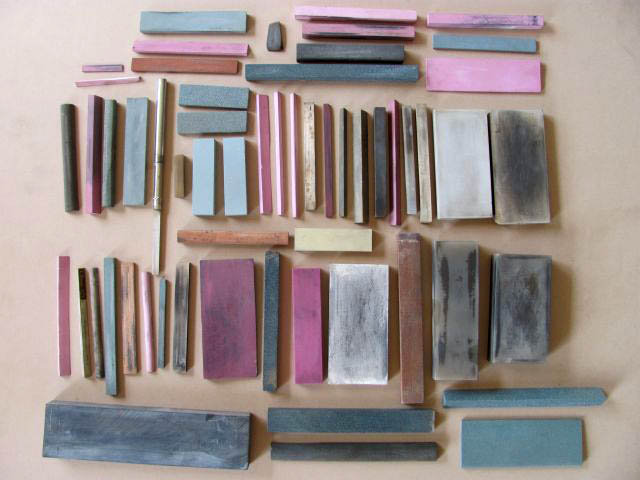

With profile chisels, especially carving ones, two sharpening stones are no longer enough, and it is necessary to have many sharpening stones of different shapes in order to reach every profile of the sharpened chisel.
For the final grinding of the carving chisels, a rag, felt or preferably a leather wheel and polishing paste are also needed.
